| In Brief |
|
The DARPA, the advanced research agency of the U.S. military, is investing in space laser projects amid growing concerns that the strategic adversaries of the United States are already developing this technology to disable satellites. B. Chance Saltzman, a general in the Space Force, announced at the Air & Space Forces Association symposium that the U.S. must strengthen its national security satellites. With China and Russia developing anti-satellite weapons, it is crucial for the U.S. to develop its own defensive options. However, the actual viability of satellites equipped with lasers remains uncertain in the short term.
The Strategic Issues of Space Lasers
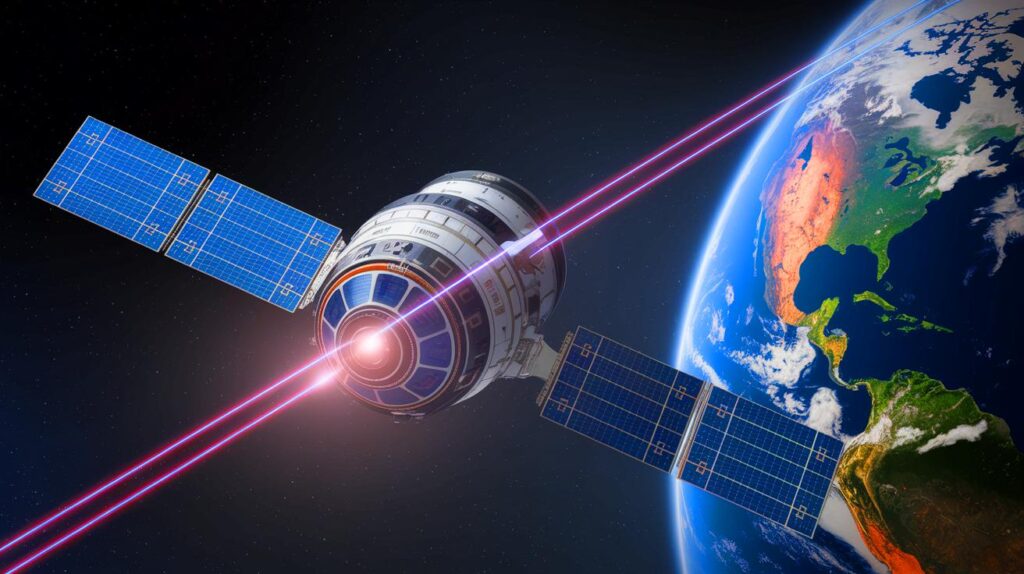
The term “space laser” often conjures images of futuristic weapons, but the reality is more nuanced. Currently, the most notable applications relate to enhancing communications. Nonetheless, military-quality laser weapon systems in development could redefine battlefields. These systems would use the light-speed communication capabilities of directed energy lasers to swiftly counter an enemy attack and disable adversary communication satellites. Many countries have satellites in orbit supporting essential military and commercial communications, ranging from navigation to missile warning. Destroying one of these satellites would disrupt crucial functions.
Concerns in the Arms Race
The DARPA is particularly concerned about Russia’s development of a nuclear anti-satellite weapon capable of blinding hundreds of satellites, according to the Center for Strategic and International Studies. China, on the other hand, operates more than 1,000 functional satellites, a third of which are dedicated to military functions such as intelligence and surveillance. Saltzman described the Chinese space targeting architecture as impressive. To enhance American communication and defense capabilities, one of the Department of Defense’s flagship projects involves establishing inter-satellite laser communications. Launched in 2022, this program has attracted major players such as SpaceX, Kuiper, Telesat, and Viasat, who support the creation of a network of satellites exchanging data at light speed.
The Technologies Behind Space Lasers
Satellites typically use slower radio frequencies, which are subject to interference and congestion. Laser communications offer a more secure and high-bandwidth method for transmitting information, paving the way for advancements in global broadband, military coordination, and even deep space exploration. While military funding supports the project, the appeal for commercial applications suggests that space lasers will become an integral component of orbital infrastructure, extending beyond a mere tool of warfare.
The Dual Nature of Laser Weapons
In addition to enhancing communications, the DARPA is designing high-energy laser systems for defensive applications. Two key projects aim to integrate these directed energy weapons into American military strategy. The High Energy Liquid Laser Area Defense System plans to adapt laser weapons to mobile platforms like aircraft and ground vehicles to shoot down enemy munitions such as rockets and artillery. The Modular Efficient Laser Technology program focuses on improving the efficiency and power of lasers through a compact and scalable system.
The potential of laser weapons is evident: they travel at the speed of light, far surpassing traditional kinetic weapons like missiles in speed and accuracy. Additionally, they do not require physical ammunition, making them a cost-effective solution for sustained operations. Laser weapons could completely disable a target in space without generating debris, an increasing problem with space junk.
Despite the promises of space lasers, challenges remain, including atmospheric interference and energy requirements. While the threats from intercontinental ballistic missiles are relatively low among technologically advanced nations, and existing defense systems proving their effectiveness, space laser defenses may not yet be as practical as other conventional deterrence methods.
The concept of laser warfare in space is appealing, but DARPA’s current focus on laser communications indicates a direction toward long-term infrastructure improvements. This could be positive. Given the potential speed and destructive power of proposed laser weapons, their eventual deployment would fundamentally and unpredictably transform modern warfare.
The DARPA’s space laser programs currently seem to be developing with an emphasis on efficiency and connectivity rather than large-scale military conflict. The day may come when directed energy weapons are commonplace, but for now, they are finding more peaceful applications in advancing satellite technology. How will these technological advancements shape our future, and what will be the ethical implications of their use?